May 1, 2024 at 11:00AM
A forensic analysis of a graph dataset of Bitcoin transactions by Elliptic and MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab revealed clusters linked to illicit activity and money laundering. The 26 GB dataset, Elliptic2, applies machine learning to detect criminal proceeds and unknown wallets, offering potential in combating financial crime using graph convolutional neural networks. The research aims to improve accuracy and expand to other blockchains.
After analyzing the meeting notes, the key takeaways are as follows:
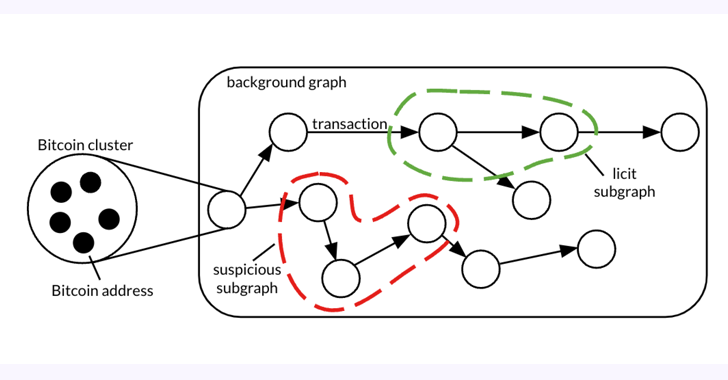
– Research collaboration between Elliptic and the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab has led to the development of Elliptic2, a 26 GB dataset containing 122K labeled subgraphs of Bitcoin clusters intended for combating financial crime using graph convolutional neural networks (GCNs).
– The use of machine learning at the subgraph level has proven effective in identifying illicit activity and money laundering patterns within the Bitcoin blockchain, particularly in distinguishing proceeds of crime and tracing funds associated with suspicious subgraphs.
– An analysis of different subgraph classification methods including GNN-Seg, Sub2Vec, and GLASS has revealed potential engagement in illegitimate activity by crypto exchange accounts and has identified known cryptocurrency laundering patterns such as peeling chains and nested services.
– The study aims to enhance the precision and accuracy of the techniques employed and extend the work to further blockchains in the future.
For further updates and exclusive content, it is suggested to follow the organization on Twitter and LinkedIn.
If you need any more information, feel free to ask!