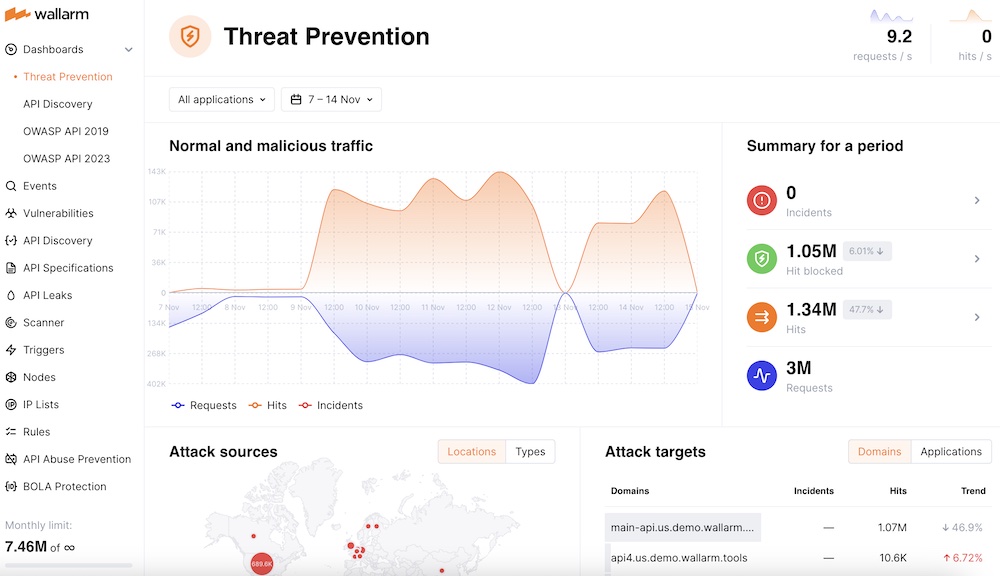
November 14, 2023 at 08:09AM
The Q3 ‘API Threatstats’ report reveals two main findings: API vulnerabilities are growing rapidly, necessitating a new compilation of the top ten API security threats. Wallarm’s report delves into different vulnerability categories with real-life examples, emphasizing their new approach to threat listing. They present the Top 10 API threats in a format similar to OWASP’s list but plan to update it four times per year instead of once every four years. Wallarm argues that their dynamic approach and inclusion of categories like injections, weak secrets and cryptography, and sessions and password management, offer a more comprehensive view of the current API threatscape. While their report may not be genuinely real-time, Wallarm’s Playground provides a real-time view of API attacks to better inform defensive strategies.
The main takeaways from the meeting notes are:
1. The number of API vulnerabilities is increasing rapidly, and as a result, there is a need for a real-time compilation of the top ten API security threats.
2. The Wallarm report discusses various vulnerability categories and provides real-life examples of their usage, including vulnerabilities in widely-used protocols like OAuth and SSO.
3. Wallarm’s Top 10 API threats list follows a format similar to OWASP Top Ten, but it is published four times a year compared to OWASP’s once every four years. It aims to provide a more dynamic and up-to-date view of API threats.
4. Wallarm identified a significant number of new vulnerabilities, with injections being identified as the number one API threat. Other categories that are not covered in the OWASP list include weak secrets and cryptography and sessions and password management.
5. Wallarm suggests that their real-time data-driven threat list complements and extends the OWASP framework by addressing unaddressed threats and vulnerabilities.
6. Although both the OWASP and Wallarm lists are snapshots in time, the Wallarm Playground on their website provides a genuinely real-time view of API attacks, which can be used to assess the current API threatscape and adjust defensive measures accordingly.